CHIEF OPERATING OFFICER/GENERAL MANAGER
Belle Haven Country Club
Alexandria, Virginia, USA
The Club
Belle Haven Country Club and the surrounding Belle Haven residential community began together in the early 1920’s when David Janney Howell, a civil engineer from Alexandria, purchased the land from owners Mrs. Thomas Wilfred Robinson, Sr. and her brothers. When the transaction was complete, Howell set up two corporations, one to construct a golf course and club and the other to develop a residential subdivision. The land was deeded to the Club on September 1, 1924.
The name Belle Haven is also part of history. When Scottish pioneers settled along the Potomac River in the early 1700’s, they named the settlement after their favorite countryman, the Earl of Belhaven. This early settlement thrived along the Potomac River as a port and was later renamed Alexandria. The Belle Haven Country Club has now become part of the fabric of Alexandria growing together throughout the 20th and into the 21st century.
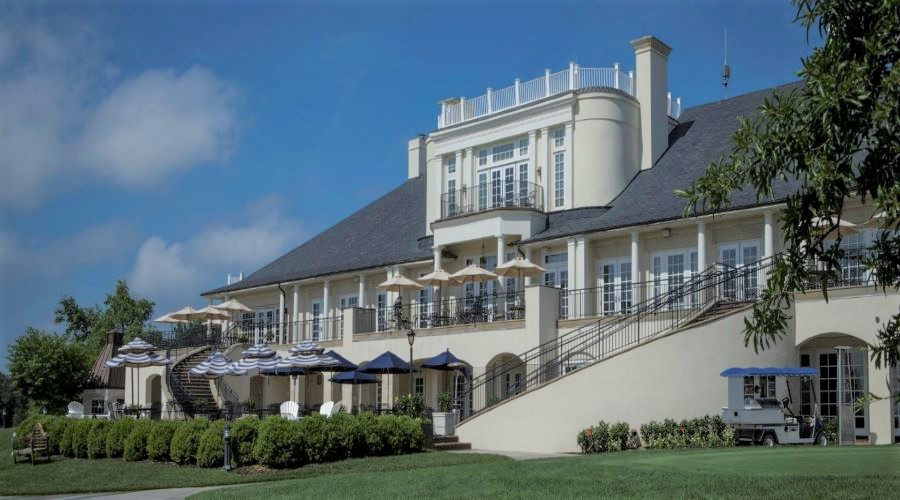
From the modest beginnings in 1924 to the new 64,000 square foot Clubhouse, Belle Haven has grown to meet the needs of its members. The Clubhouse offers a variety of dining options including formal and informal restaurants, family dining, Bar and Bar Lounge, Terrace and Patio dining along with the Hilliard Room and the relaxing 19th Hole. For special occasions and meetings, Belle Haven offers a beautiful ballroom with views of the golf course. We host banquets and meetings in our spacious Potomac Room with spectacular views of the Potomac River.
Our Athletic Facility houses a complete fitness center and aerobics room along with five indoor DecoTurf tennis courts, a Tennis Pro Shop, Children’s Activity Center, seasonal swimming pool, men’s and ladies’ locker rooms with steam and sauna, a year-round restaurant known as the Center Court Cafe and the famous outdoor Sharks Cafe open throughout the summer season. We have eight outdoor, clay tennis courts and two seasonal platform tennis courts available for our members and their guests.
Vision Statement
To provide a lifelong haven for our members, their families and guests where they can enjoy social, dining and recreational activities in outstanding facilities with a professional staff, consistent with the expectations of our culture and traditions.
Mission Statement
To be a premier, full service, family oriented, private country club committed to excellence.
Belle Haven Country Club Overview
- 1105 Members
- Initiation Fee ($85,000)
- Annual Dues ($8,676)
- $12.78M Gross Volume
- $6.12M Annual Dues
- $2.32M F&B Volume
- $6.39M Gross Payroll
- 244 Employees
- 13 Board Members
- Average age of members is 59
The COO/GM Position
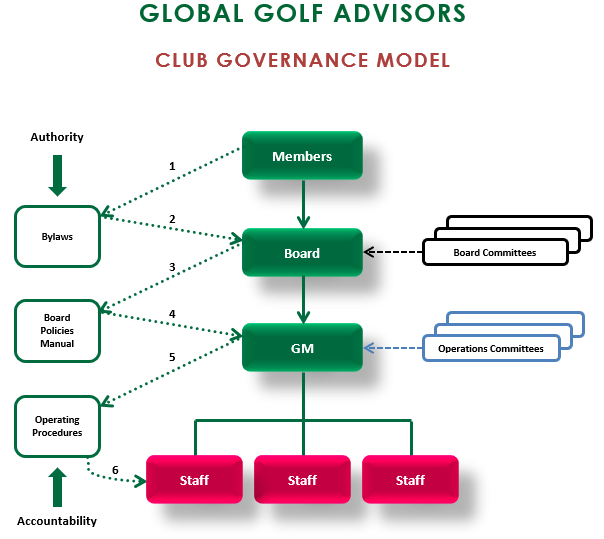
The General Manager/Chief Operating Officer manages all aspects of the club including its activities and the relationships between the club and its Board of Directors, members, guests, employees, community, government, and industry. Coordinate and administer the club’s policies as defined by its Board of Directors. Develop operating policies and procedures and direct the work of all department managers. Implement and monitor the budget, monitor the quality of the club’s products and services and ensure maximum member and guest satisfaction. Secure and protect the club’s assets including facilities and equipment.
Primary Responsibilities:
- Coordinate the development and execution of the club’s long-range and annual business plans to achieve the mission of the club
- Prepare comprehensive operating plans and budgets, obtain approval from the board, and operate in accordance with approved budgets
- Maintain a long-term capital budget to assure the sustained material condition of all physical assets of the club
- Plan, develop and approve specific operational policies, programs, procedures, methods, rules and regulations in concert with board-approved policies
- Direct the recruiting and training of all staff
- Establish employee rules and regulations, work schedules, internal controls, and a performance appraisal system
- Assure that the highest standards are set and achieved in providing member service and satisfaction
- Ensure that the club is operated in accordance with all applicable local, state, and federal laws
- Ensure compliance with regulatory and other governmental agencies that have oversight of various club assets and operations
- Provide the board and committees with relevant information on trends and developments in the club/residential community business
- Ensure that the committees established by the board are well-supported and operate in accordance with board-approved policies and directives
- Oversee security, risk management, and health and safety programs to ensure that measures are in place to protect members, employees, staff, and club physical assets
- Ensure that the board is thoroughly informed on the status of club operations, member satisfaction, and financial performance
- Provide a comprehensive communications program that keeps all appropriate constituencies informed on relevant matters
- Interact with local community leaders and organizations
- Perform other duties and functions as the club board may direct that are consistent with this job description
Direct Reports:
- CFO
- Director, Member Services
- Golf Course Superintendent
- Head Golf Professional
- Assistant General Manager
- Director of Membership and Communication
- Director of Tennis
Core Leadership Competencies:
- Ability to define a simple and understandable vision of success for the management team
- Ability to see the big picture, take stock, identify problems/needs, and conceptualize solutions/strategies
- Ability to focus on the essentials, to attend to detail, and to follow through on decisions
- Ability to create a sense of followership among subordinates
- Ability to attract and develop a strong supporting management team capable of ensuring a smooth transfer of responsibility when tasks are delegated.
- Ability to demonstrate a strong member satisfaction ethic and to interact with the membership in a frequent and friendly manner
- Ability to articulate the highest performance and ethical standards, demand compliance, and move swiftly and positively when corrective action is warranted
- Ability to cope with day-to-day pressures and maintain a healthy and positive culture
Candidate Qualifications:
- A minimum of 7 years of progressive leadership and management experience in a private club, hospitality, and leisure environment.
- A Bachelor’s Degree from an accredited college or university, preferably in Hospitality Management or Business.
- Certified Club Manager (CCM) or in active pursuit of designation preferred.
Note: A pre-employment drug screen and background check will be required.
Salary and Benefits:
Salary is open and commensurate with qualifications and experience. The Club offers an excellent bonus and benefit package.
Inquiries:
IMPORTANT: Interested candidates should submit résumés along with a detailed cover letter which addresses the qualifications and describes your alignment/experience with the prescribed position by Wednesday, October 27, 2021.
Documents must be saved and emailed in Word or PDF format (save as “Last Name, First Name, Belle Haven GM/COO Cover Letter” and “Last Name, First Name, Belle Haven GM/COO Resume”) respectively to execsearchus@ggapartners.com. Please email résumé with references.
Lead Search Executive
For more information about Belle Haven Country Club, please visit www.bellehavencc.com