In the ever-changing private club industry, organizations must continually ask themselves, “Are we managing operations to the best of our ability?” Peter Drucker, widely recognized as the founder of modern management said, “You can’t manage what you don’t measure.” Drucker’s words hold true today as the field of data science evolves at an increasingly fast pace. While the club industry has generally adopted data-driven approaches, our experience at GGA Partners highlights three common metrics that, when utilized effectively, are powerful contributors to success:
Revisiting member resignations
Clubs should aim to take an integrated view of their membership and while many have made great efforts to better track active membership profiles, there are significant opportunities in evaluating thorough data on resigned members. Clubs interested in reducing membership attrition are well-served to obtain a clear picture of resigned members. Collecting information on resigned members actually begins with appropriately tracking the members’ joining date and demographic information. With this, clubs are not only able to analyze what the typical lifecycle of membership is, but also how this lifecycle may differ across a variety of demographics. With this method, a club will obtain more insightful findings than a general resignation metric. For example, a club could determine when female members resign and whether this differs to male members, the conversion rates of intermediate category members to full, or whether members within certain geographic areas showcase distinct resignation patterns. Utilizing this lifecycle analysis, clubs can subsequently evaluate current active memberships and analyze who may be nearing the historical “end of membership” timeline. Digging deeper, if a club tracks the historical spend and usage habits of members leading up to their resignation, there comes an opportunity to utilize analytics to observe active members who display similar spend and usage patterns exhibited by resigned members (i.e., reductions in spend and usage).
Diving into usage details
Another area of opportunity is increased tracking of detailed amenity utilization statistics, such as rounds played, fitness check-ins, tennis court bookings, and food and beverage covers. As an effect of the COVID-19 pandemic, many clubs adapted their booking technology to meet both safety regulations (where necessary) and membership demand.
Numerous clubs currently track this information on an aggregate basis (which is a great start) but incredible value comes from tracking the data on a per-member and time-associated basis. For example, for a private golf club, knowing how many rounds of golf your club saw in a year is valuable, but being able to assess which groups of membership played more than others during certain time frames offers a much more focused and actionable scope (particularly if utilization concerns continue to impact membership dissatisfaction across private clubs globally). The same impact could be had for a private multi-sport facility with tennis or fitness bookings. To generate this level of insight, clubs must track any sort of booking to the given member and attach a time with said booking. For example, if a specific member is playing a tennis match at 9:30am on a Saturday, this would be tracked within the club’s internal systems. At the end of the month, the club could export all match data and run various analyses, such as which members played the most, what are the busiest days and times, were there days of the week that would benefit from having additional programming to reduce higher-capacity times, and so on.

Managing membership movements
At a basic level, clubs should be confident in their knowledge of year-end membership category counts. With this information, assessments can be made on how certain categories have changed within a year, and then further investigated. Delving beyond the basics are those who have accurately tracked new sales, resignations and transfers within each category. Clubs should consider collecting and reporting data according to membership categories. Looking at the table below, including the previous year-end count to act as the baseline moving forward and the most recent year-end count provides context on increases and decreases. New sales, resignations, and transfers in and out for each membership category are also included, and updated throughout the year for easy input.
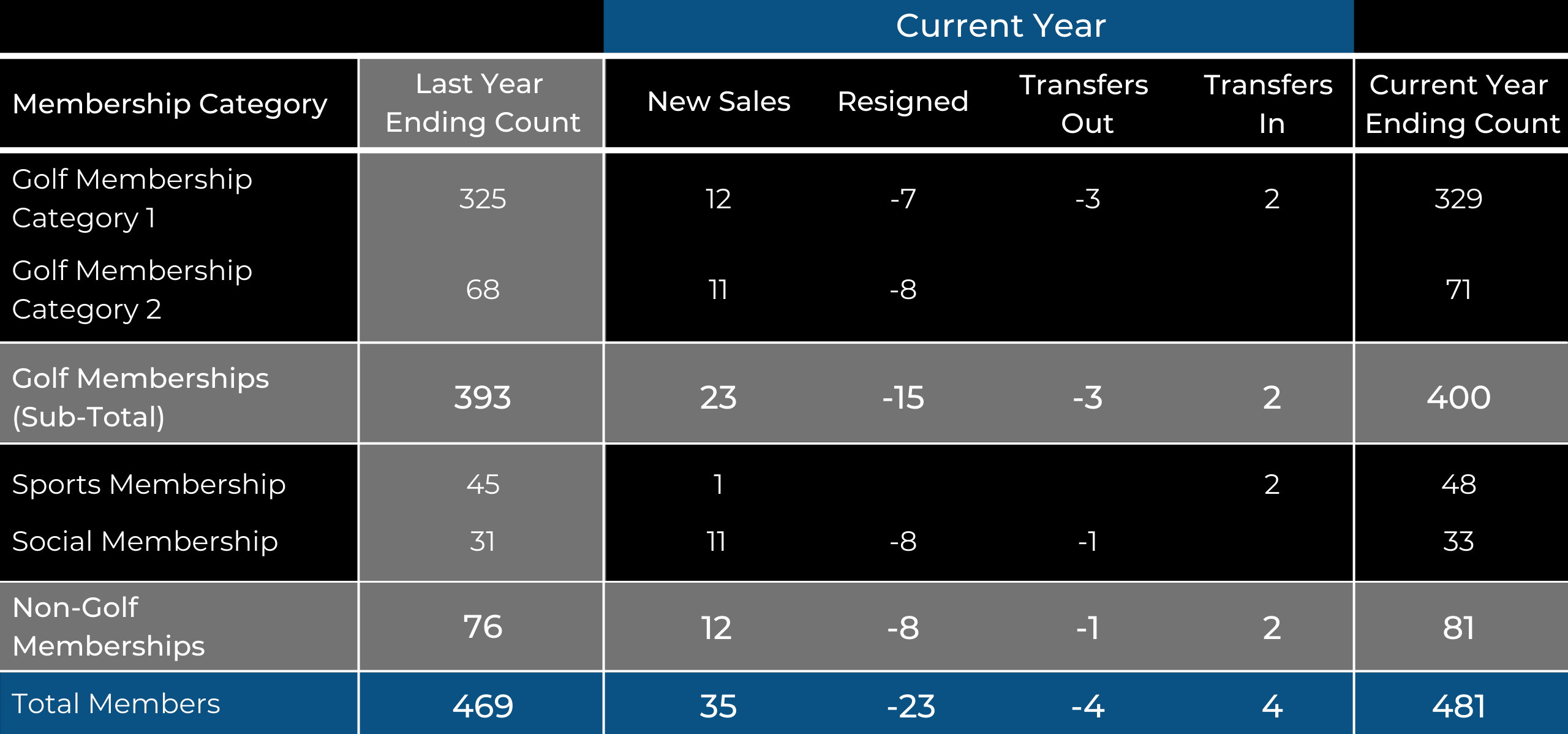
This comprehensive analysis allows clubs a detailed look at how membership is truly moving throughout any given year. For example, a category may appear steady from a year-over-year perspective, but upon further analysis, the reality showcases an incredible amount of pressure on new membership sales due to increased member transfers or resignations. With this level of insight, the club can then investigate why there are so many members moving out of this category and take actionable steps to stabilize its membership.
Improving and sustaining business performance is always top of mind for club leaders. A deeper approach to data and analytics plays a critical role in maximizing performance across club operations. Increased awareness into trends emerging from resigned members, the usage patterns of specific membership groups, and how members are migrating will lead to better understanding of the membership, and more effective actions taken by the club.
How our research & analytics professionals can help
Research and analytics are fundamental to GGA Partners’ proven approach to analyzing club performance and to continually improving the tools and solutions we offer our clients. With a team of professionals that carry over 28 years of experience in the golf, private club, and leisure industries, we can show your club how to leverage data and analytics to drive success.
Contact a GGA Partners professional today for more information.